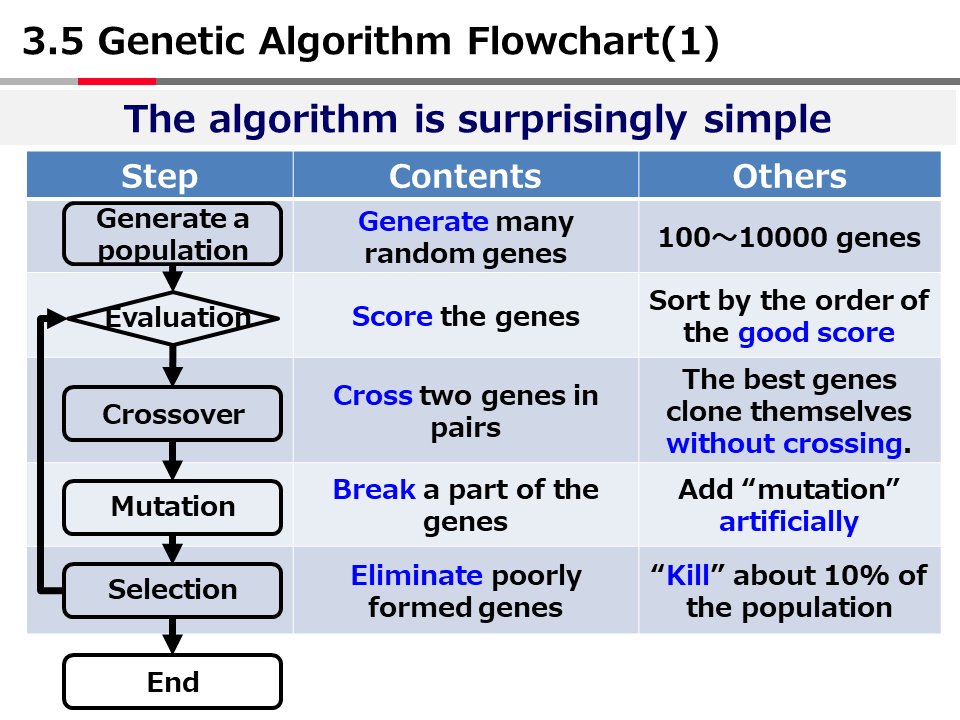
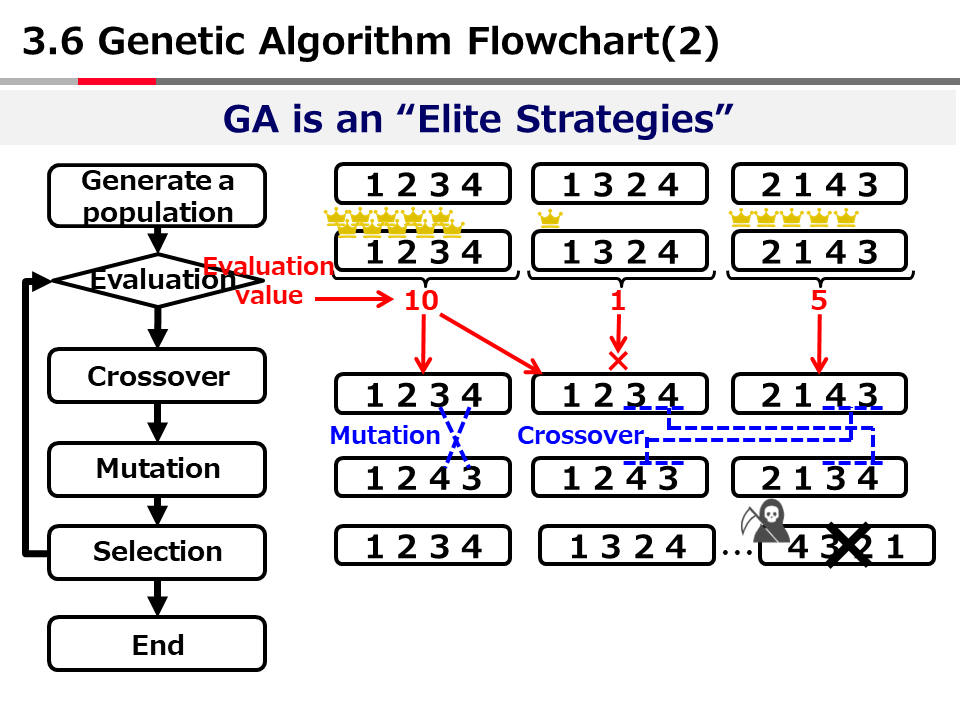
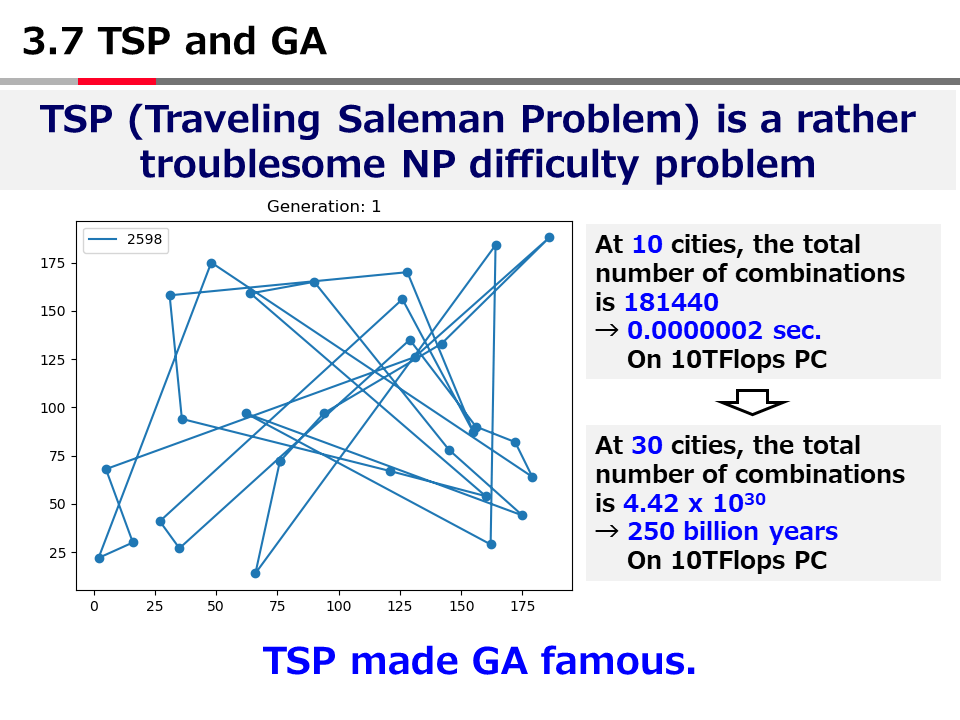
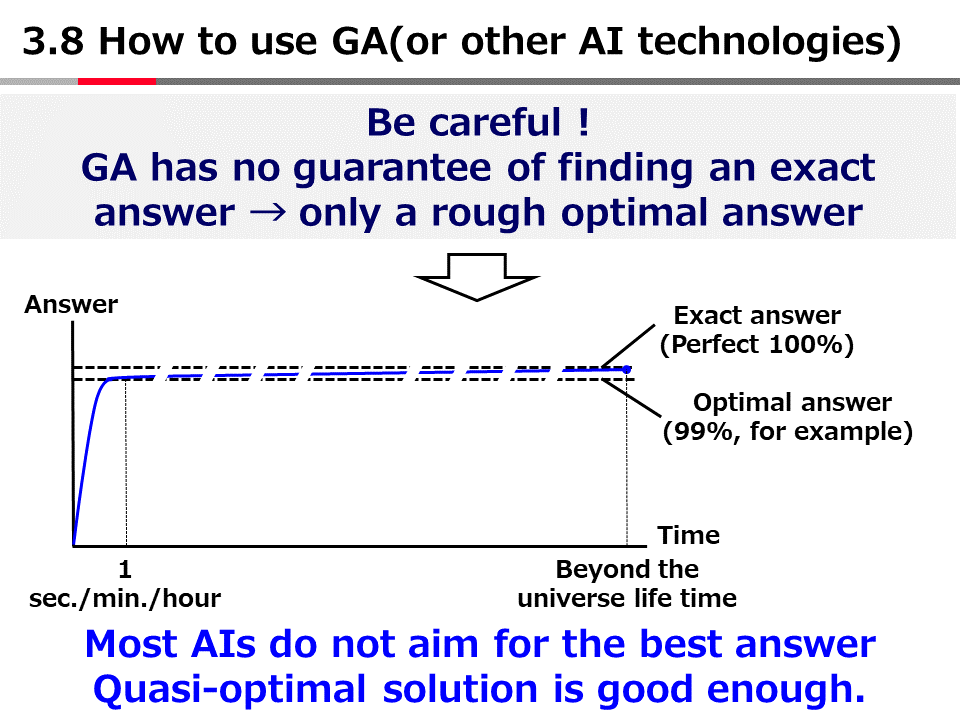
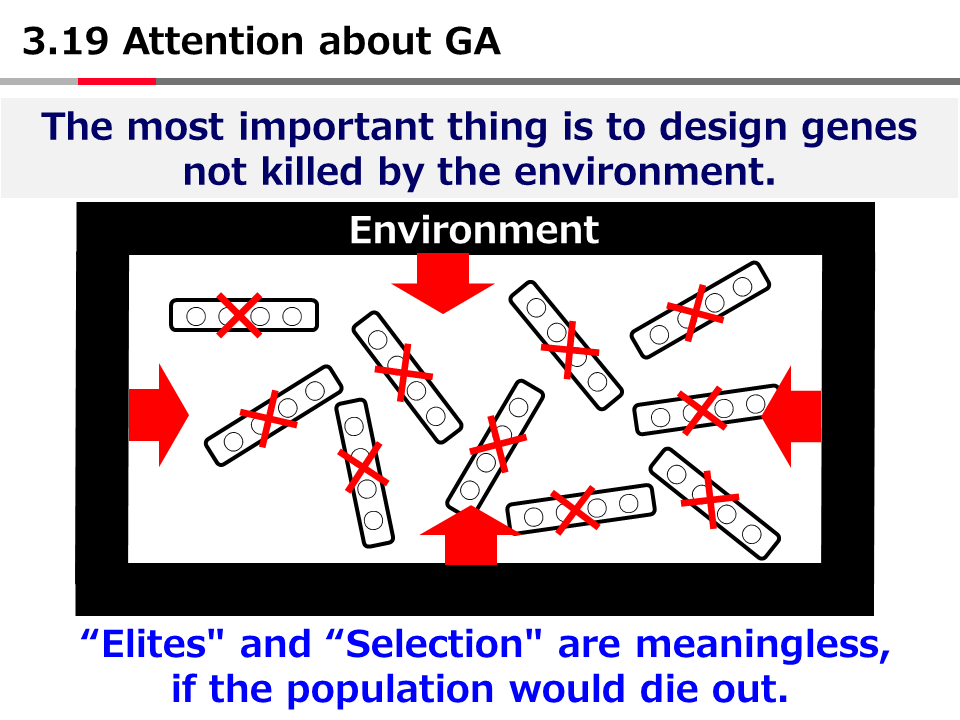
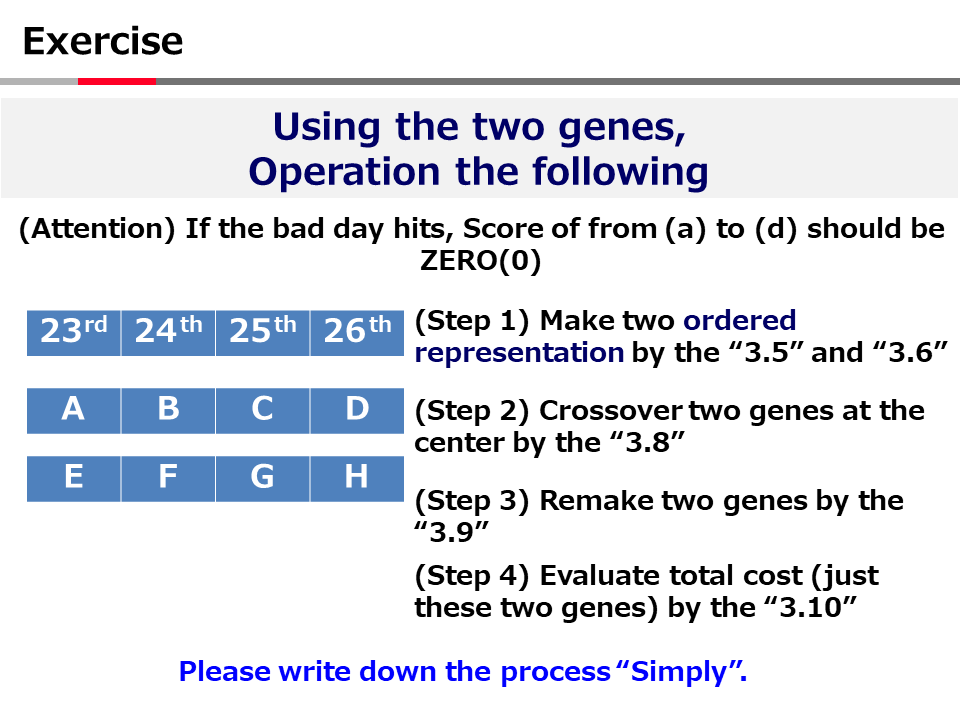
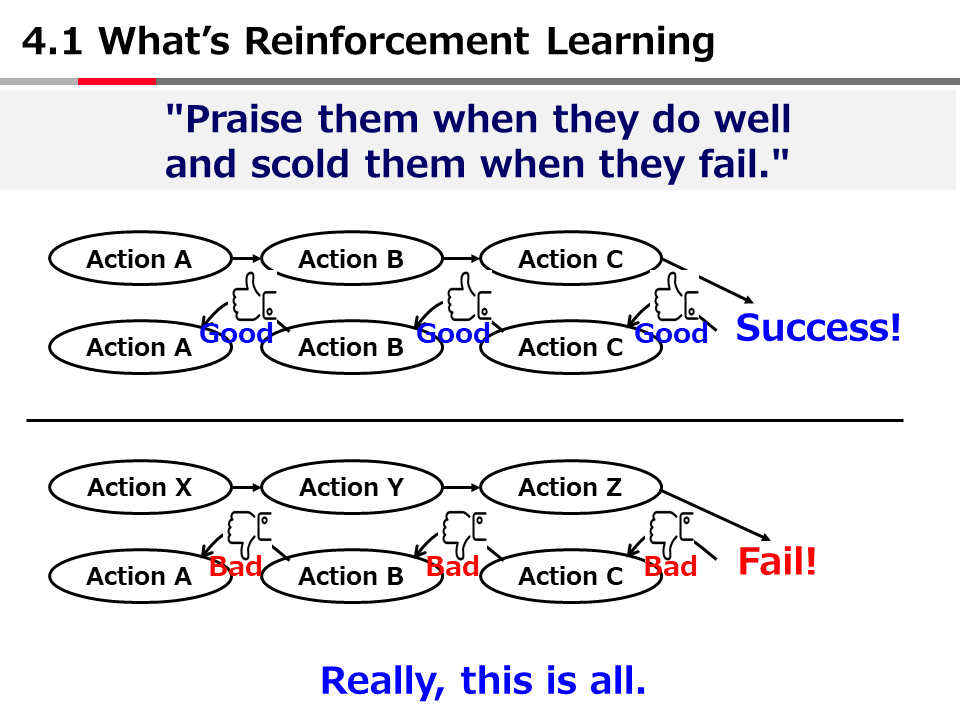
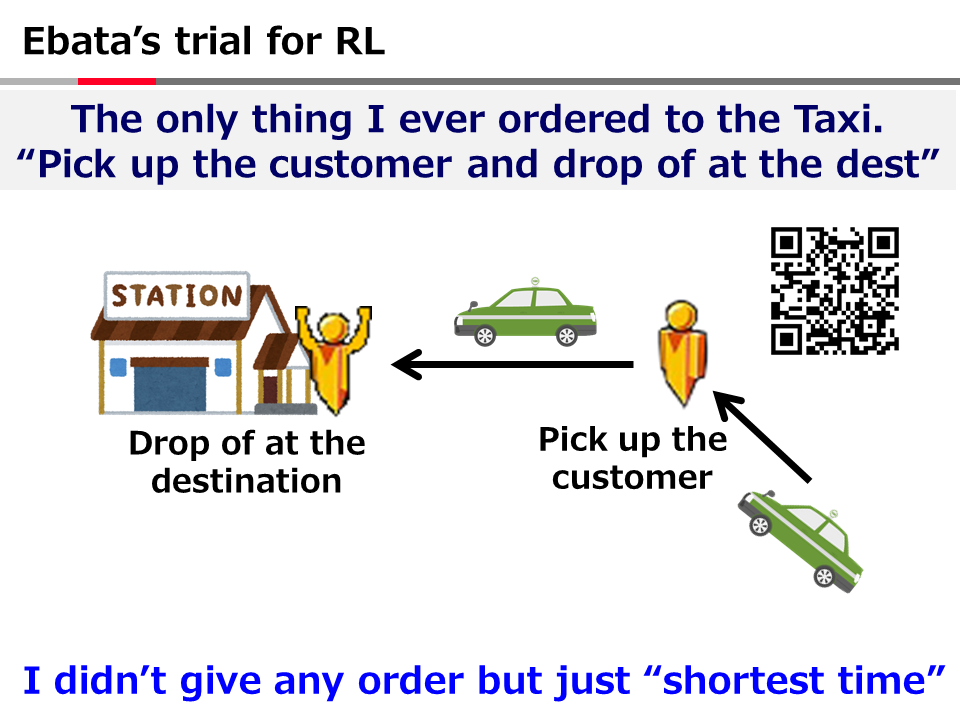
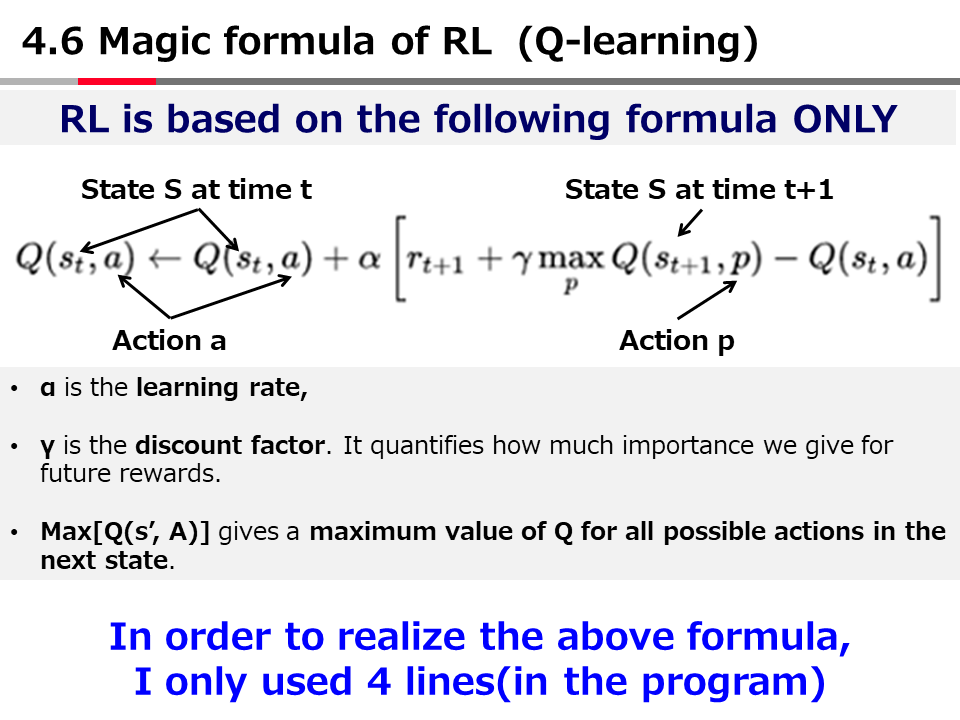
英語論文の現在形と過去形の使い分け
person agent か、human agentか?
person:普段「1人の人」を指す。
persons:フォーマルな場面で使う。
people:普段「複数の人」を指す
human:神や動物、ロボットではなく「人間」。
man:「男性」「人」「人類」。最近は「人」「人類」の意味で使うのは避ける傾向にある。
guy、fellow、bloke:口語で「やつ」。
"human agent"で良いように思う。
「自律判断」という英訳で悩む → ここは、"Google裁定"に任せる
"autonomous behavior":149,000
"autonomous decision":383,000
"self-determination": 510,000,000
"autonomous decision" & "algorithm": 82,200
"autonomous behavior algorithm" 146
"autonomous decision" & "algorithm":82,200
"autonomous decision algorithm":1,300
"self-determination" & "algorithm": 421,000
"self-determination algorithm":1,520
結論: "self-determination"が勝者だと思うけど、論文の下書きみたら、"behavioral psychology"が乱発されていた。今、ここで、これを換えると、前後の文章も替えなければならないので、本件は放置する。
住民 resident と inhabitant の違い
どちらも住民という意味ですが
resident は、特定の地域の居住者のことを指し、一時居住者も含むのに対し、
inhabitant は、その地域に長く住む集団に属するものを指します。
どちらも通例では、sをつけた複数形で使われることが多いようです。
resident は、「住民」の他に「居住者」とも訳されますし、名詞の他に形容詞としても使われますが、inhabitant は、名詞のみで、「住民」の他に「定住者」や「生息動物」という意味にもなります。この動詞形は inhabit となり、「に居住している」「に宿る」「巣食う」という意味です。
「課題」をどう訳すか?
→"技術課題"は、"technical problems"でいいみたい(problemを使うと、"問題点"みたいに聞こえるので、"challenge"を使いたくなるけど)
https://www.bizmates.jp/blog/kadai-eigo/
Problem(課題、問題)
Problemは「解決すべき問題」という意味で表現したい時に使います。不利益や不都合を来たす物事を指します。
[例文1]
This is a problem our company needs to work to resolve in the long term.
これは我が社が長期的に取り組まなくてはならない課題です。
[例文2]
Does anyone have a good idea to resolve the problem?
この課題を解決するためのいいアイディアはありますか?
[例文3]
The biggest problem of this project is the lack of human resources.
このプロジェクトの一番大きな課題は、人材が不足していることです。
Task(課題)
Taskは「やらなければならない作業・仕事」というニュアンスです。日常的な業務レベルで与えられた軽めの仕事や宿題を指します。
[例文1]
The only task I have left for this week is making my presentation slides.
今週残る課題はプレゼンテーションの資料作りです。
[例文2]
Thanks for helping me out. I was able to complete my task by the due date.
手伝ってくさってありがとうございました。なんとか期日までに課題を終えられました。
[例文3]
The president gave me a task to come up with a better marketing message.
社長からより良いマーケティングメッセージを策定するように、という課題をいただきました。
Assignment(課題)
AssignmentはTaskに似た意味合いを持ちますが、「任務」や「任された仕事」と、大きめの課題といたニュアンスです。上司から割り当てられた課題は、このAssignmentで表現します。ビジネスシーンだけでなく、学校でも宿題の意味で使われる表現です。
[例文1]
Let’s complete this assignment with everyone in the department.
この課題は部署全員で協力して完了させましょう。
[例文2]
I got a new assignment from my boss. I need to get it done within this year.
上司から新しい課題を渡されました。今年中に完了しなければなりません。
[例文3]
I’d like to give this assignment to Gabriel. It’s not going to be easy, but I think it will help him gain experience.
この課題はガブリエルにアサインしようと思います。難しいでしょうが、彼にはいい経験になると思います。
Issue(課題)
Issueは「議論すべき事象や問題」というニュアンスの表現です。Problemはそのもの自体がトラブルになりかねない問題を意味しますが、Issueはその事柄について賛成する人・反対する人に二分されている場合など、明らかに問題と言いきれない時や、角が立たないよう「問題」と呼ぶのを避けたい時に使います。
[例文1]
We should resolve this issue ASAP.
この課題は早急に解決したいですね。
[例文2]
The rising costs of our factories in Asia are a serious issue for our company.
アジア圏の工場でのコストの増加は弊社にとって大きな課題となっています。
[例文3]
At our company, we are taking social issues such as SDGs seriously.
弊社では、SDGsをはじめとした社会の課題に熱心に取り組んでいます。
Business(課題)
Businessは一般的に「仕事・事業・業務」という意味で使われますが、「片付けなければならない仕事」という意味でも使用されます。頻繁に使われる表現ではありませんが、これもissue のように婉曲な「問題」の言い方になります。
[例文1]
That is none of your business. I will take care of it.
それは私の課題なので責任を持って終わらせます。
[例文2]
I have some business I really need to take care of by the end of the day.
どうしても今日中に片付けなくてはならない課題があります。
[例文3]
It looks like we’ve got some business to do.
どうやら課題がでてきたようですね。