出展はこちら→ https://content.connect.panasonic.com/jp-ja/fai/file/39018

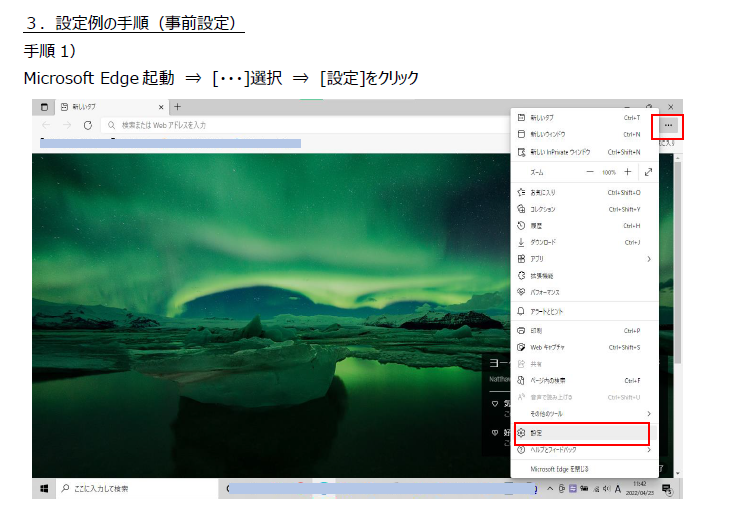
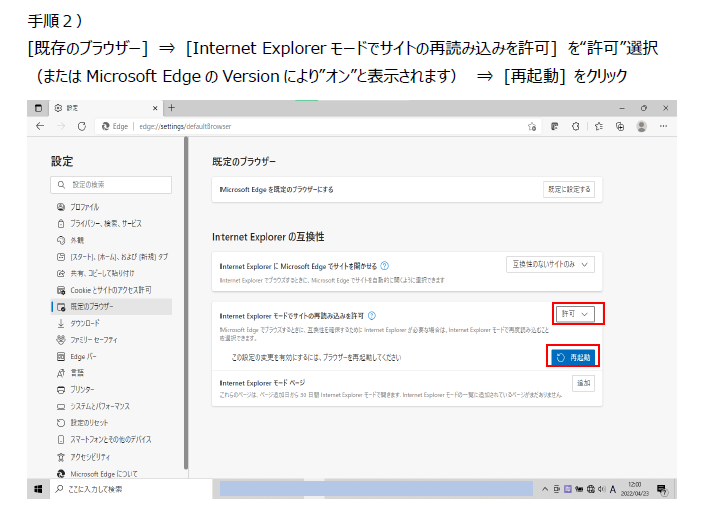
admin/jvc で、 JVC HD IP Camera VN-H68 が出てくる
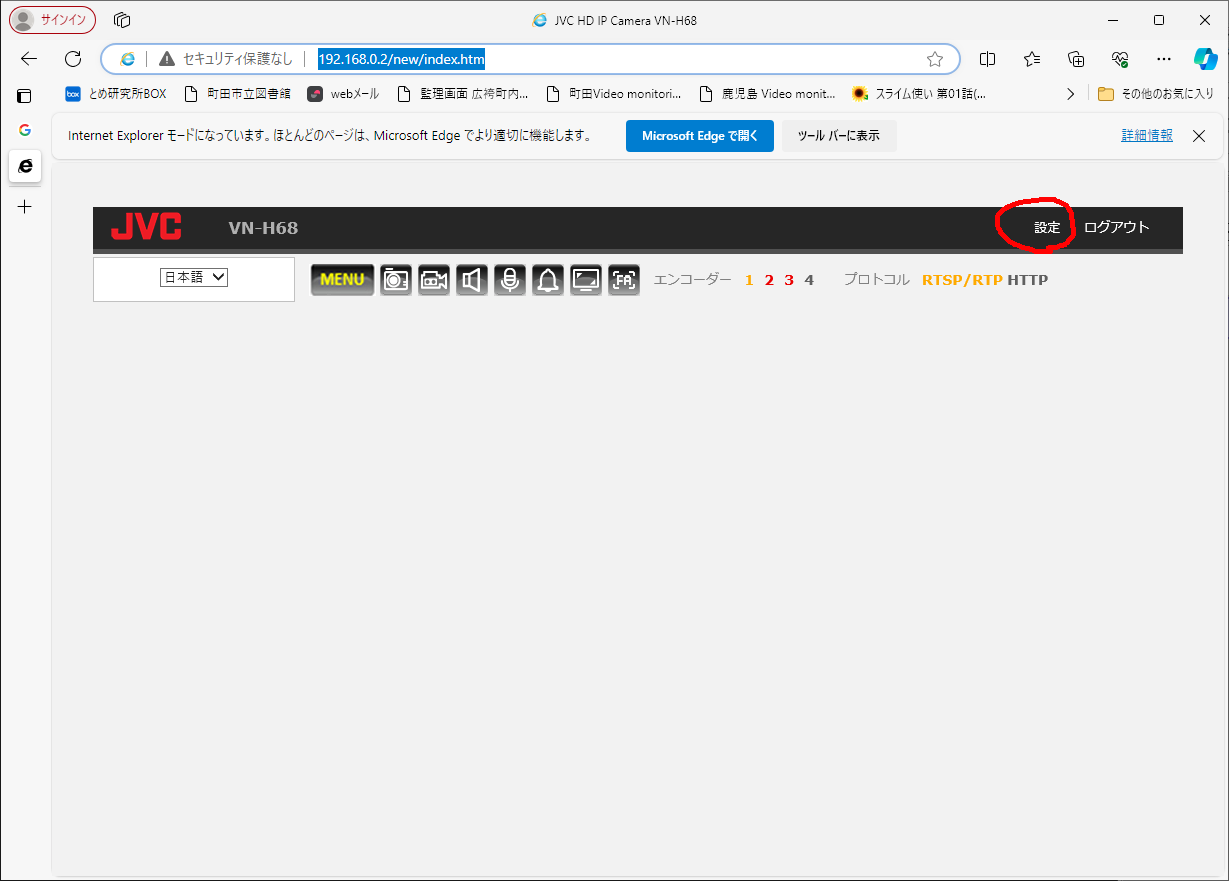
「設定」を押す。
以上
江端智一のホームページ
出展はこちら→ https://content.connect.panasonic.com/jp-ja/fai/file/39018



admin/jvc で、 JVC HD IP Camera VN-H68 が出てくる

「設定」を押す。

以上
Keyword:USB LAN ehternet アダプタ ubuntu etc netplan
(1)>ip addrで、
8: enx207bd2222d29: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000 link/ether 20:7b:d2:22:2d:29 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
みたいな奴をみつける
(2)/etc/netplan/99_config.yamlで、以下のよう書き替える

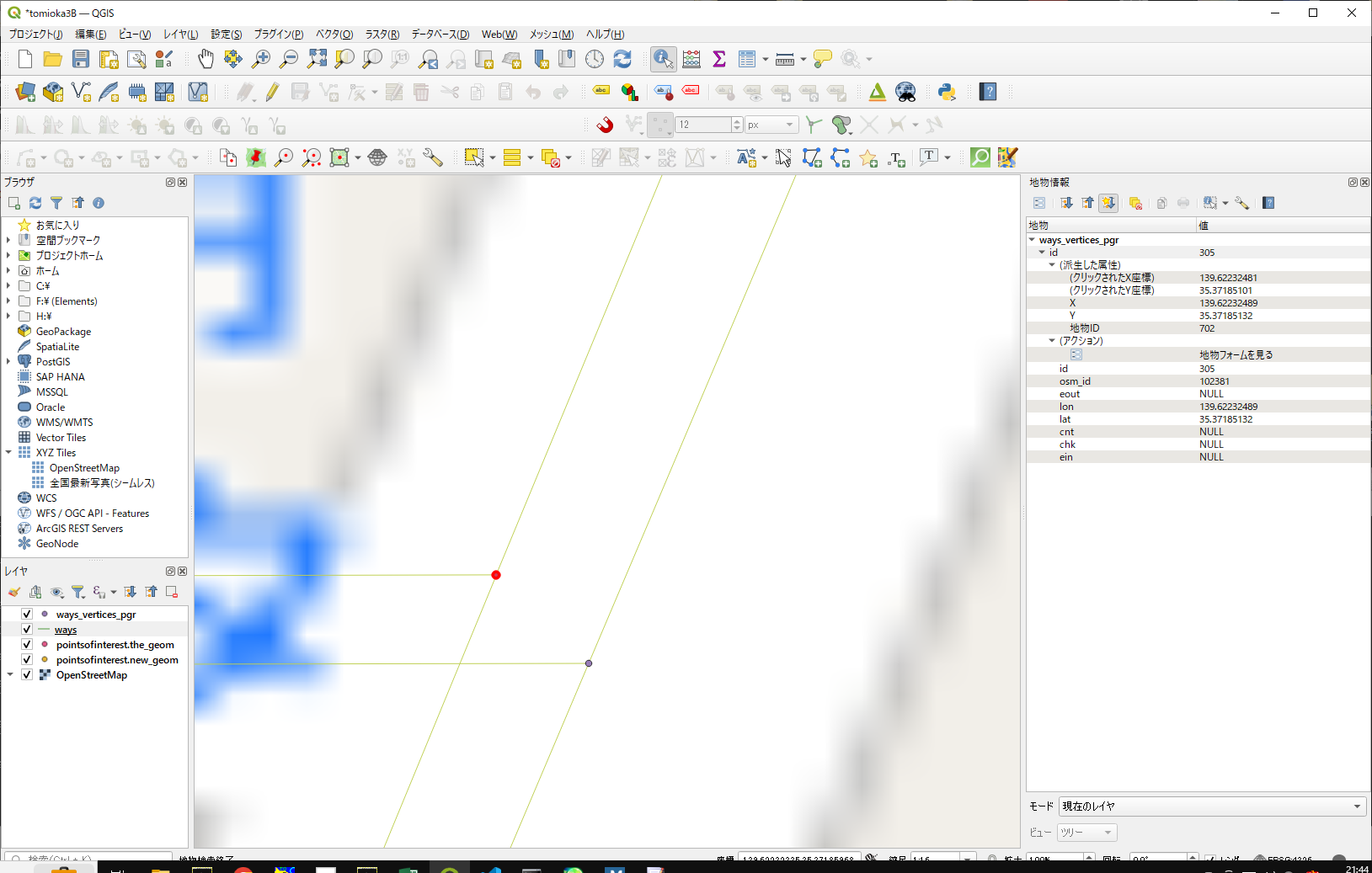
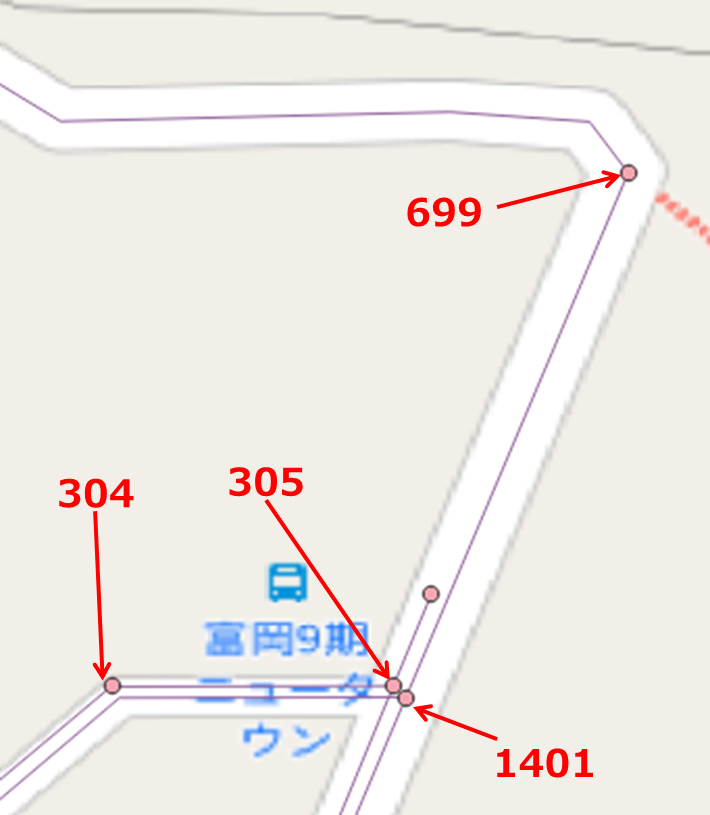
まず、この2つの点は、どっちが、私(江端)が追加したノードだったのかを思い出すことにします。
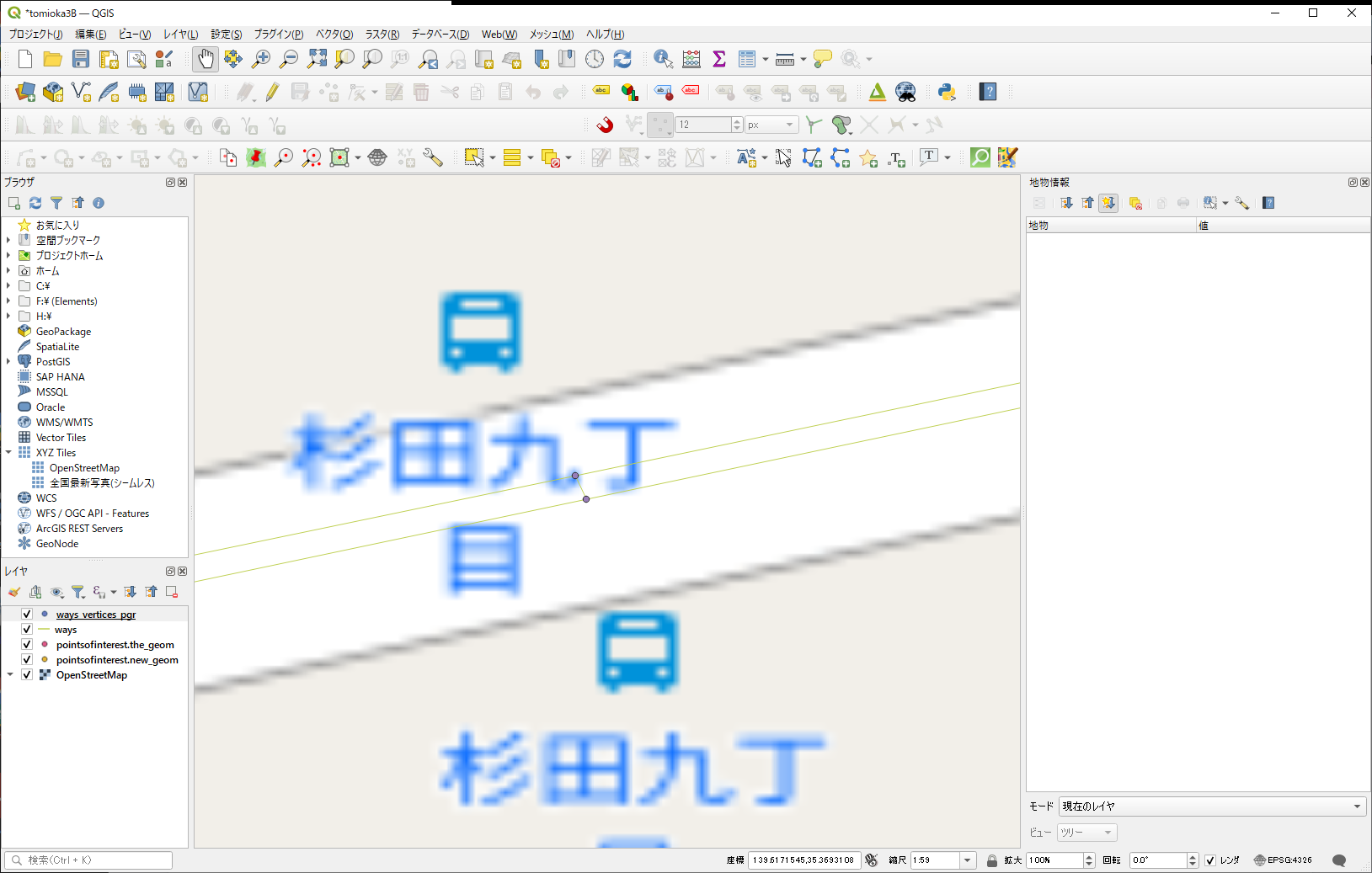
上のノードは、こんな風
id番号が若いから、こっちが私が作った方で、まあ、間違いないでしょう。
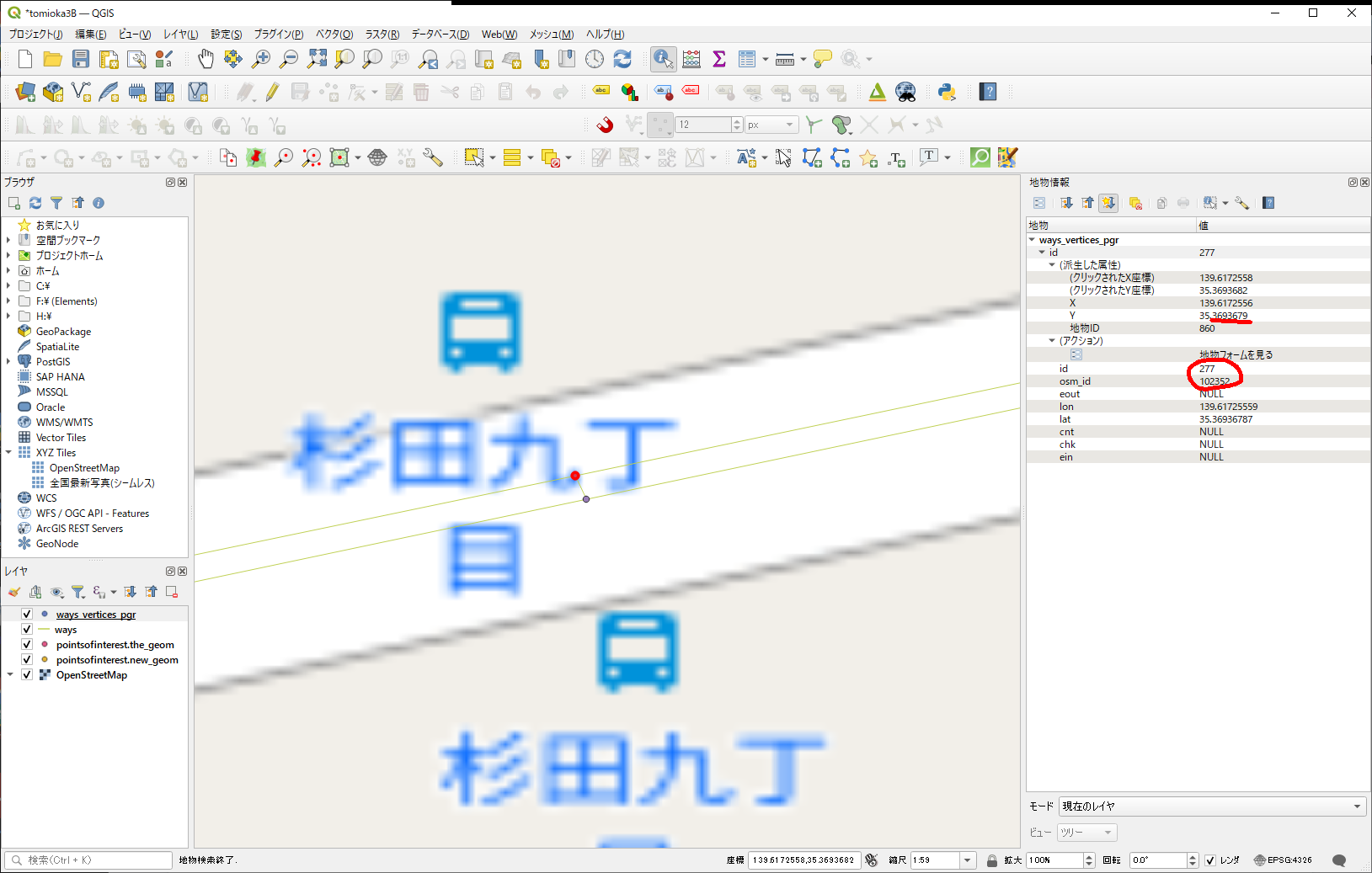
念の為、もう一方も確認。
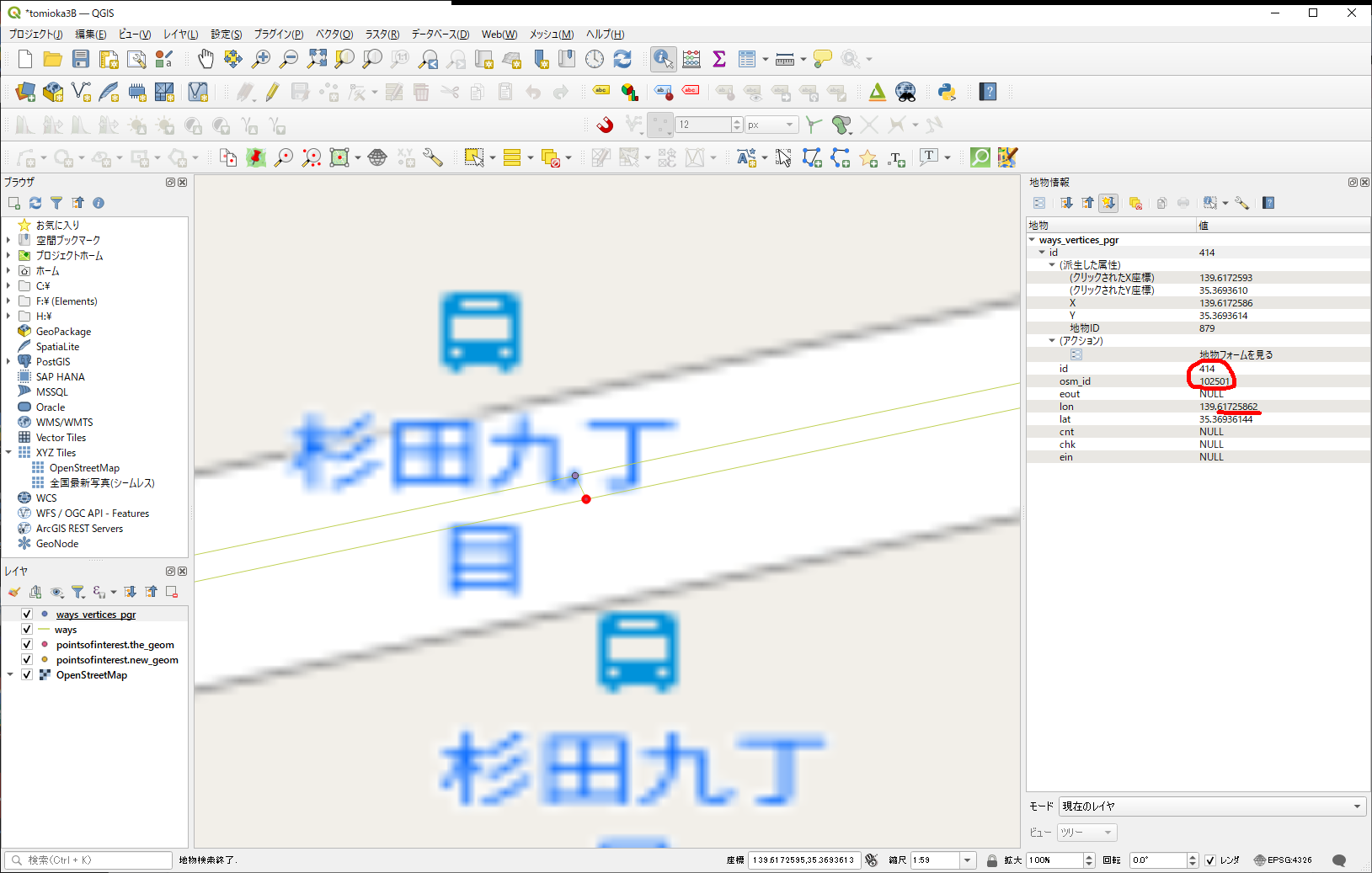
こちもID番号若いけど、以前管理した番号とは違うみたいだから、こっちが既存のノードであろう、とする。
これを私が結線した時に作った道路が、これ。
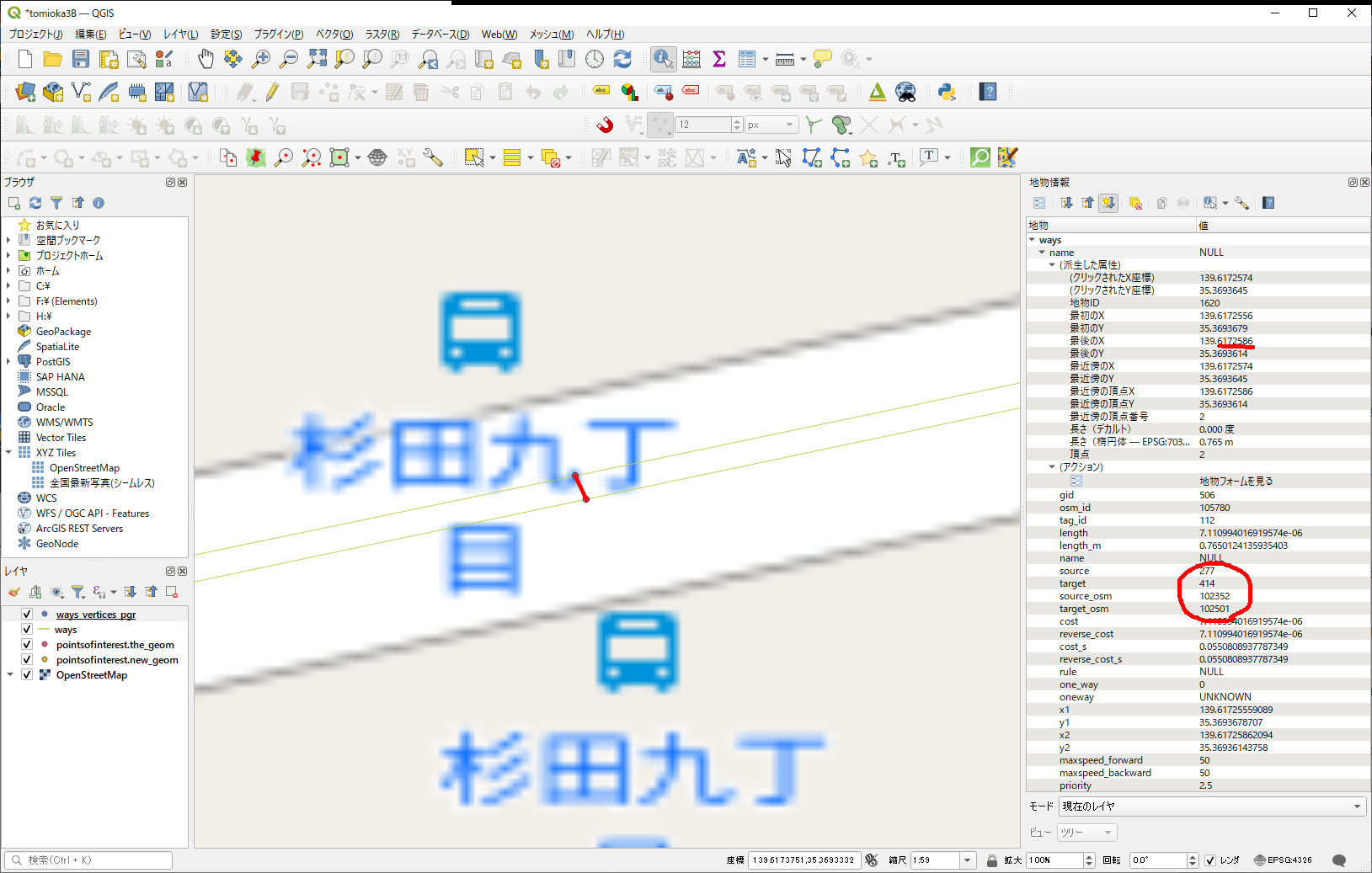
結線の情報は、source,target, source_osm, target_osmで入っているので、少なくともノード間の結線であれば、ここの加工だけで何とかなるんじゃないかな、と。
で、ここの部分のエントリーを見てみたら、こんな感じでした。(tomioka_db_c_trialの方で確認中)
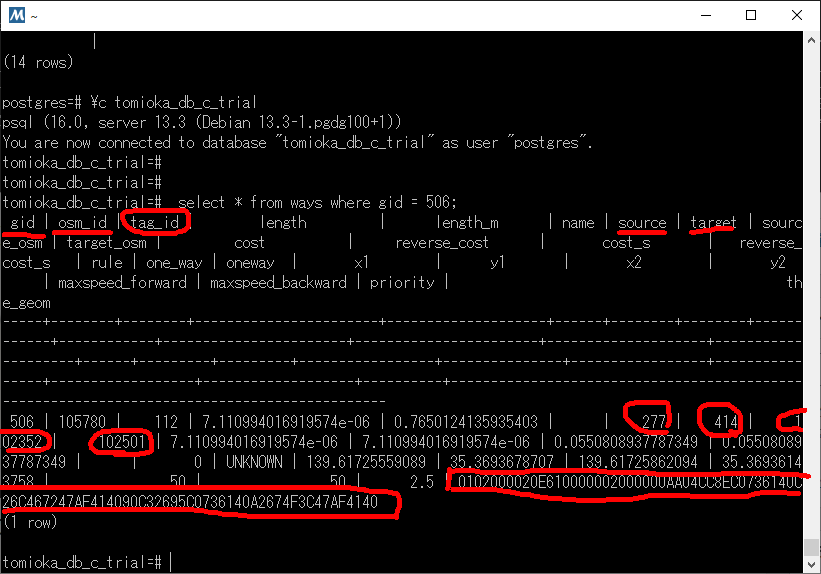
gid、osm_id →新規の番号を適当に付ける
source, target, source_osm, target_osm は、これから結線するノード番号を記載する。(sourceが、江端が作成したNodeになっている)
と、まあ、ここまではいいとして、tag_idってなんだろう。あと、the_geomをどうしようかなぁ。
QGIS使ってtag_id = 112 だけを表示して調べてみたけど、私が手を入れたところに(も)出てきているようなので、何も分からないまま 112 を使うことにする。
さて、次に問題は、the_geomである。これは面倒くさい。多分デタラメな値を入れても大丈夫だとは思うが、念を入れておきたい。
と、2点の座標を結ぶ直線であることが分かった。
そこで、以下のプログラムを作成してみた。
/*
c:\users\ebata\tomika3b\src\others\main31.go
go run main31.go
*/
package main
import (
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"github.com/twpayne/go-geom"
"github.com/twpayne/go-geom/encoding/wkb"
)
func main() {
// 2つの緯度経度ポイント
//coordinates := [][]float64{{139.6917, 35.6895}, {-74.006, 40.7128}}
coordinates := [][]float64{{139.61725559089, 35.3693678707}, {139.61725862094, 35.36936143758}}
//coordinates := [][]float64{{139.61725862094, 35.36936143758}, {139.61725559089, 35.3693678707}}
// Geometryの作成
lineString := geom.NewLineStringFlat(geom.XY, []float64{coordinates[0][0], coordinates[0][1], coordinates[1][0], coordinates[1][1]})
// WKB形式に変換
wkbBytes, err := wkb.Marshal(lineString, wkb.NDR)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
return
}
// WKB形式を16進数文字列に変換
wkbHex := hex.EncodeToString(wkbBytes)
// 出力
fmt.Println(wkbHex)
}さて、このプログラムからから、
0102000020E610000002000000AA04CC8EC0736140C26C467247AF414090C32695C0736140A2674F3C47AF4140
を作れるかな?
coordinates := [][]float64{{139.61725559089, 35.3693678707}, {139.61725862094, 35.36936143758}}
としたら、
ベース: 0102000020E610000002000000AA04CC8EC0736140C26C467247AF414090C32695C0736140A2674F3C47AF4140
作成: 01020| |0000002000000aa04cc8ec0736140c26c467247af414090c32695c0736140a2674f3c47af4140
一部欠けているが、一致している。
では、逆転させてみよう。
coordinates := [][]float64{{139.61725862094, 35.36936143758}, {139.61725559089, 35.3693678707}}
としたら、
ベース: 0102000020E610000002000000AA04CC8EC0736140C26C467247AF414090C32695C0736140A2674F3C47AF4140
作成: 000000000200000002406173c08ecc04aa4041af4772466cc2406173c09526c3904041af473c4f67a2
こっちは、不一致が多いようです。
でも geomの長さが違うと思い、ChatGPTに尋ねてみたところ、以下のように言われました。
-----
では、本命。
 この2点間を結線する、をやってみます。
この2点間を結線する、をやってみます。
coordinates := [][]float64{{139.62232489, 35.37185132}, {139.62233160, 35.37184490}}
で計算したところ、
今回は、この2点間を繋ぐ、wayのオブジェクトを作れば良いだけなので、基本的にはwayのエントリーを一つ追加するだけで足りるはず。
(1 row)
空き番号となっているgidは1984
空き番号となっているosm_idは、現在104088(と同じ桁であれば)、104090あたりが良さそう
INSERT INTO ways (gid, osm_id, tag_id, length, length_m, name, source, target, source_osm, target_osm, cost, reverse_cost, cost_s, reverse_cost_s, rule, one_way, oneway, x1, y1, x2, y2, maxspeed_forward, maxspeed_backward, priority, the_geom)
VALUES (1984, 104090, 112, 7.110994016919574e-06, 0.7650124135935403,NULL, 305 , 1401, 102381, 4095221163, 7.110994016919574e-06, 7.110994016919574e-06, 0.0550808937787349, 0.0550808937787349, NULL, 0, 'UNKNOWN', 139.62232489, 35.37185132, 139.62233160, 35.37184490, 50, 50, 2.5, '0102000000020000002d41e315ea736140ed2ff5d298af41408ea8f523ea7361409a571a9d98af4140');
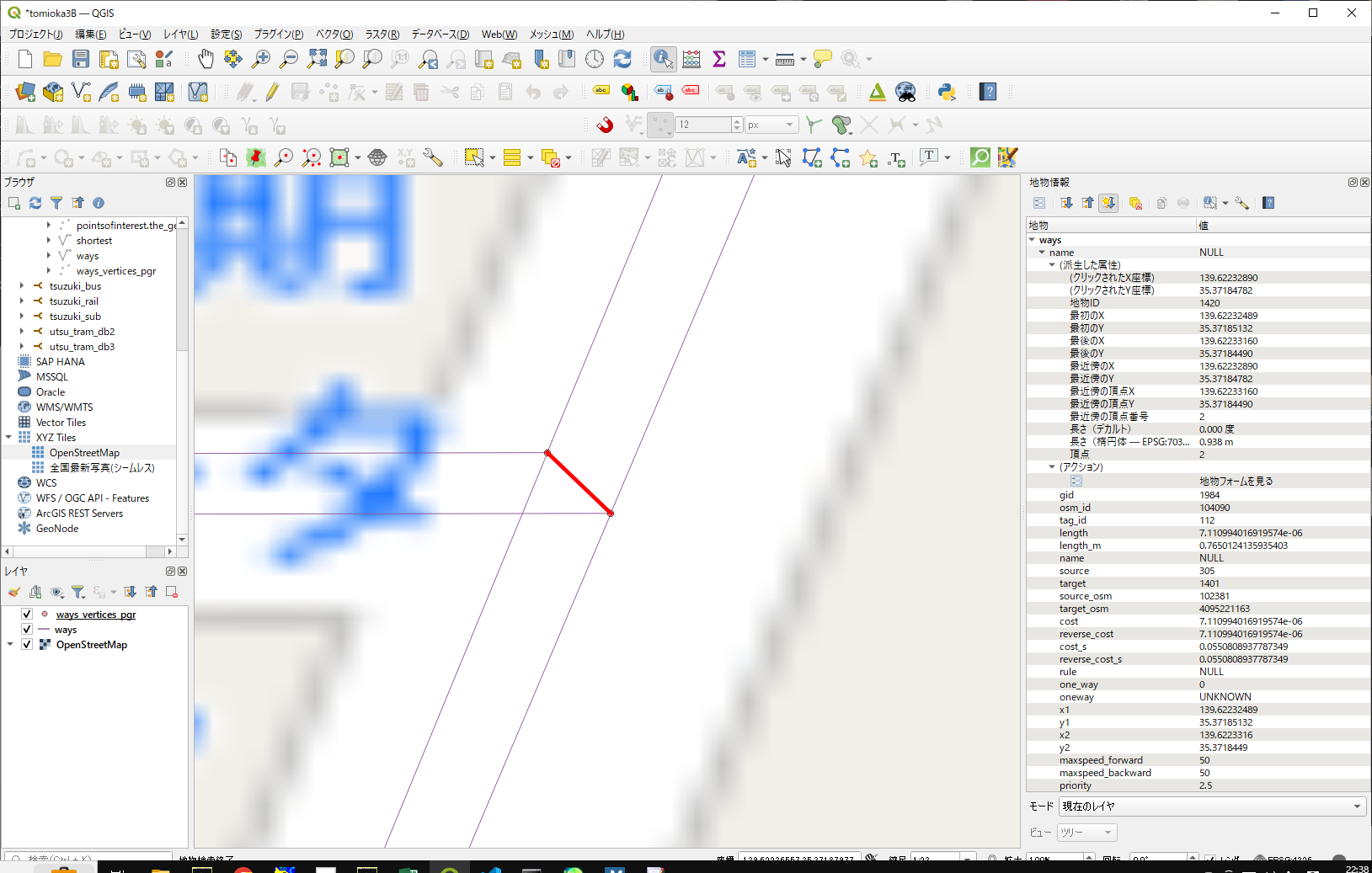
結線されたようです。
では、ちゃんとダイクストラで繋がるのかを確認してみます。
バス時刻表を手動でCSVファイルにしてから、バスの運行テーブルに書き換えるプログラム(1行分だけだけど)
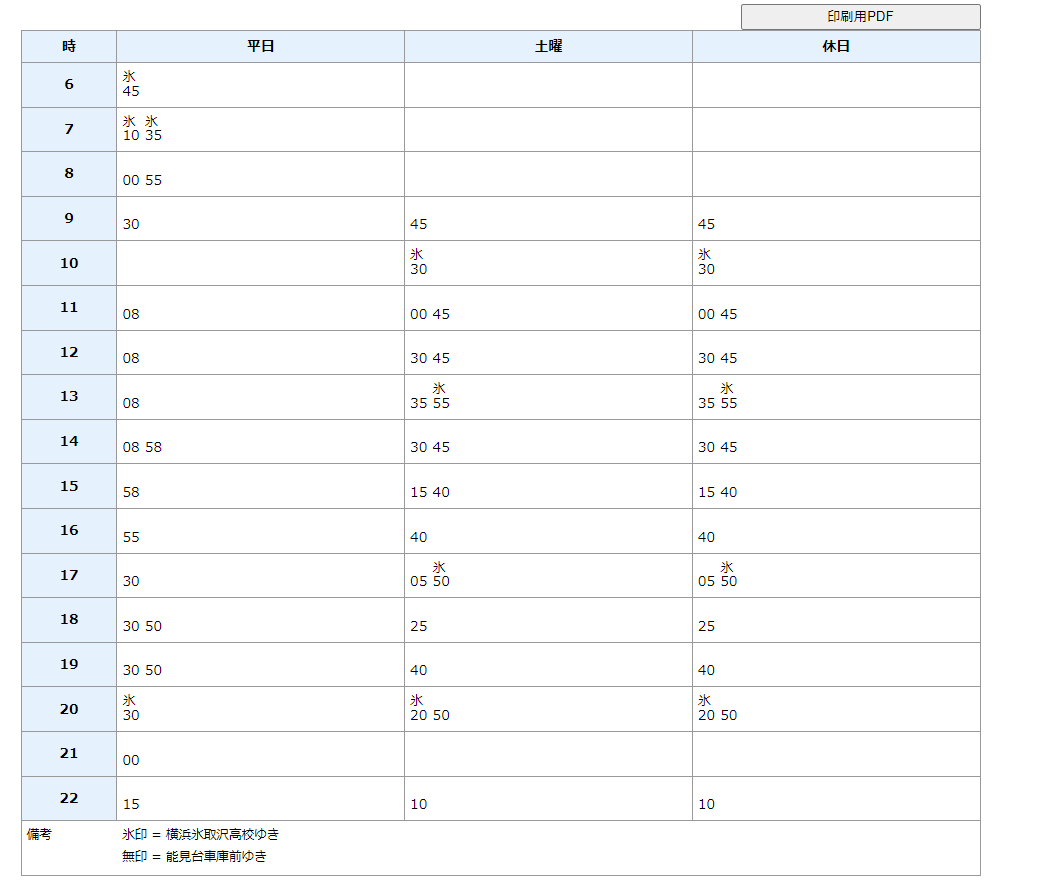
を、エクセルに貼りつけて、
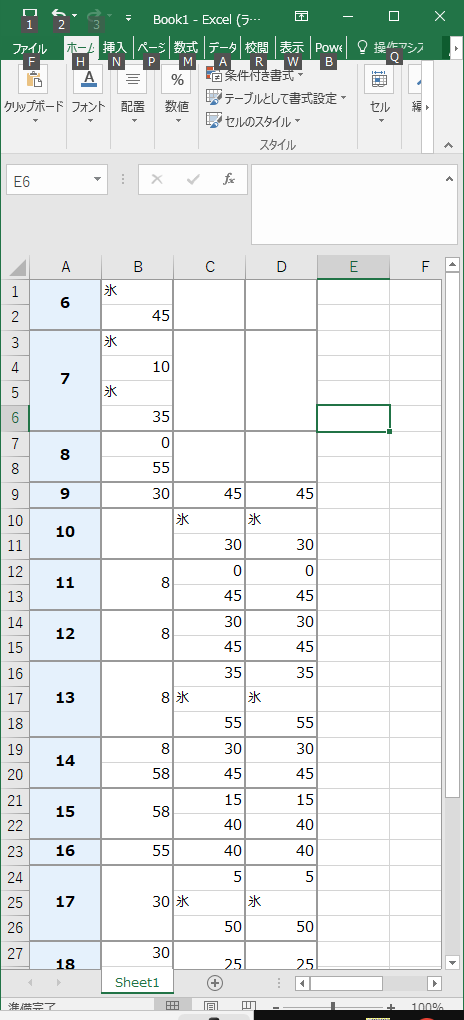
csvでinput.csvという名前でセーブしてから、go run main30.go で実行すると、
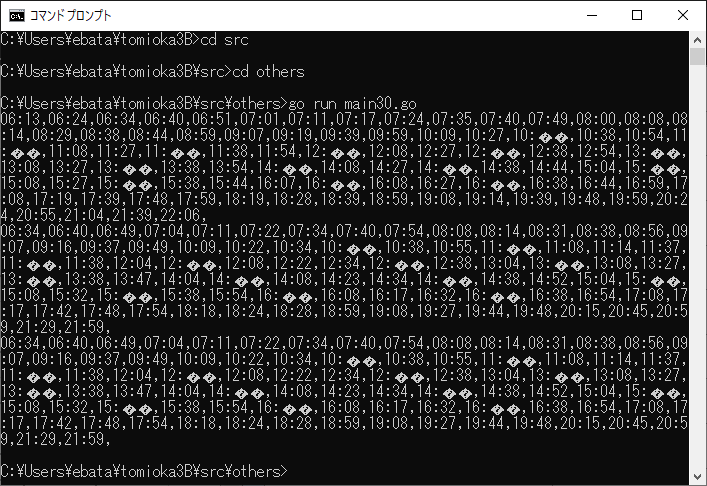
てな感じで、平日、土曜、休日単位のテーブル(の1行)になる。
// バス時刻表を手動でCSVファイルにしてから、バスの運行テーブルに書き換えるプログラム
// c:\users\ebata\tomioka3B\others>go run main30.go
package main
import (
"encoding/csv"
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
// 入力ファイルと出力ファイルのパス
inputFile := "input.csv"
// CSVファイルを読み込む
csvFile, err := os.Open(inputFile)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
return
}
defer csvFile.Close()
reader := csv.NewReader(csvFile)
records, err := reader.ReadAll()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
return
}
// 出力するデータを格納するスライス
var hour string
for k := 1; k < 4; k++ {
for _, row := range records {
if row[0] != "" {
hour = row[0]
}
if row[k] != "" {
fmt.Printf("%02s:%02s,", hour, row[k])
}
}
fmt.Println()
}
}
バスの時刻表
今、私は、「現実の街と同じ街を、コンピュータの中に作りこむ」をやっています。
I am currently working on "creating a city on the computer identical to an actual town.
詳しいことは割愛しますが、これを完成させて動かさないと、大学院を卒業できません。
I will spare you the details, but if I do not complete and move this, I will not graduate from college.
週末はこの作業で、全部の時間が溶けていきます。
This process melts away the entire weekend.
恐しく面倒くさい作業なのに、学術的には語るべき内容がない ―― 苦労談ならいくらでも語れるんですけどね。
It's a horrible and annoying process, but there's no academic content. Even if I could tell you all about the hard work.
面倒なのは、ゲームのように「自由に街を設計する」のではなく、「現実にある街を反映させる」ことです。
What is troublesome is not "freely designing a city" as in a game but "building in" a city that exists in reality.
言うまでもなく、"ワープ"とか"どこでもドア"のような架空の設定は許されません。
Fictitious settings such as "warps" or "doors to anywhere" are prohibited.
『一体、どこの誰が、こんな地図情報 ―― どう考えたって"内部情報"だよなぁ ―― を入手して、OpenStreetMapに展開したんだろう』
-----
会社の仕事でやっていた時は、もっと短期間で試作システムを作ることができたように思うのですが、今は、"亀"のような遅さです。
When I was working for the company, I thought I could create a prototype system in a much shorter time, but now it is as slow as a "turtle.
あらためて『なんで、こんなに時間がかかるんだろう』と考えてみて、当たり前の事実に気がつきました。
I thought again, 'Why is it taking so long?' and realized an obvious fact.
―― 辛い作業を、"他人"に押しつけてきたから
"I've been putting the hard work on "others"."
"他人"とは、例えば、会社の同僚や、ソフト外注さんです。
Others" are, for example, colleagues in the company or software subcontractors.
そういう人たちの圧倒的な支えがあったら、今と比較して、"光の速度"のような構築ができていた。
I had the overwhelming support of such people, so I would have been able to build at the "speed of light" compared to today.
しかし、私が大学でやっている研究対象のシステムの作り手は、私ひとりだけです。
However, I am the sole creator of the system, which is the subject of my research at the university.
そりゃ、"亀"のような速度になるのは、当然です。
Naturally, the speed would be like that of a tortoise.
私、ちょくちょく「一人でがんばっている」ような記述をしていましたが ―― 当たり前ですが ―― 一人でできることなんて、高が知れているんですよね。
I have often described myself as "working hard on my own," but there is only so much one person can do.
-----
バーチャルの街とは言え、これを一人で作るのは、本当に大変です。
Even though it is a virtual city, it is a real challenge to create this all by oneself.
この街、本当に完成するのか ―― そう考えると、怖くて眠れない日があります。
This city, will it be completed -- there are days when I can't sleep because I'm so scared to think about it.
これは、「一人でがんばっている」と思い上がっていた私への「報い」なのかもしれません。
This may be a "retaliation" for my presumption that I was doing my best on my own.
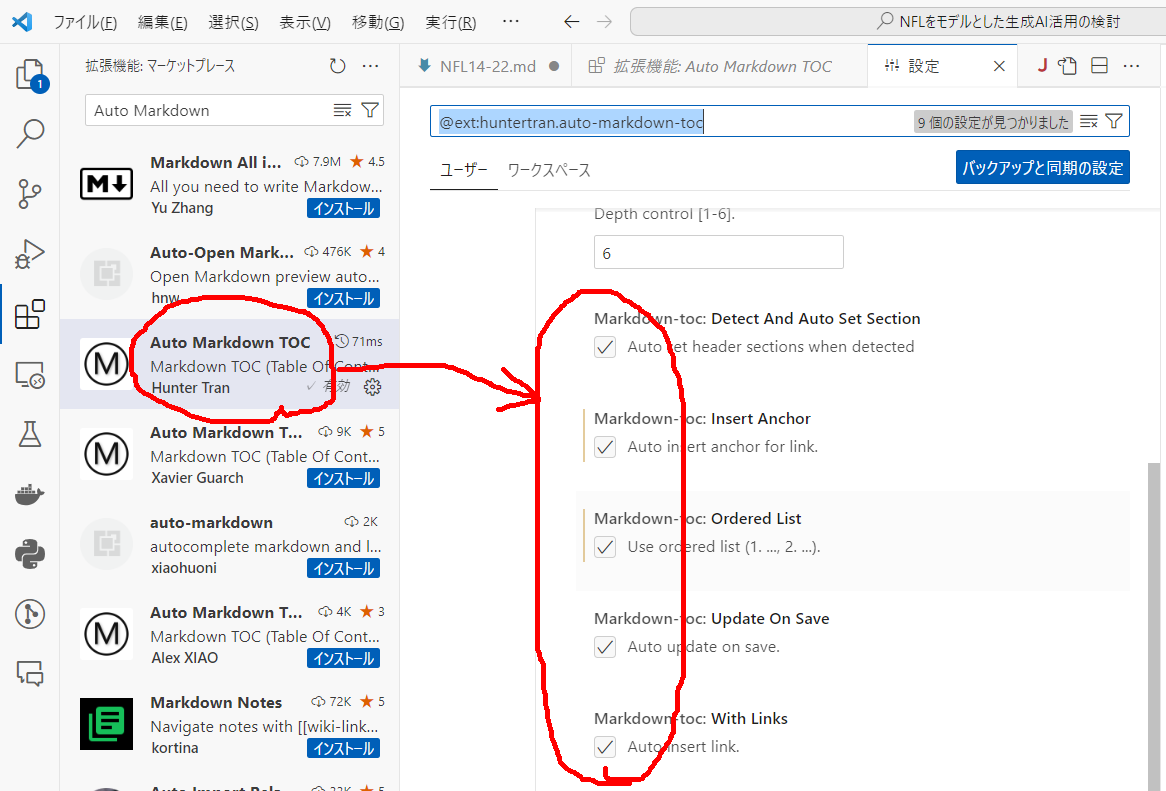
VSCode の Auto Markdownで目次や章番号が出てこなくなったら、とにかく、拡張機能の全部にチェックをつける
以下のGo言語プログラムで、"small2_bus_data.csv"が1行のみの
1, 93, 139.62957005198, 35.36604342344, 12:55:00
を使って、を読み込ませたのですが、その結果が
1 0 0 12:55:00 [{1 0001-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC {0 0}}]
となってしまいます。
package main
import (
"encoding/csv"
"fmt"
"os"
"strconv"
"time"
)
// 緯度経度の型定義
type LatLng struct {
Lat, Lng float64
}
// 時間と緯度経度の情報を持つ構造体
type BusData struct {
NodeID int
Time time.Time
Location LatLng
}
func main() {
// CSVファイルを開く
file, err := os.Open("small2_bus_data.csv")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
// CSVファイルの内容をパースする
reader := csv.NewReader(file)
records, err := reader.ReadAll()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
return
}
// データを格納するためのスライス
var busData []BusData
// CSVの各行を処理する
for _, record := range records {
nodeID, _ := strconv.Atoi(record[0])
lng, _ := strconv.ParseFloat(record[2], 64)
lat, _ := strconv.ParseFloat(record[3], 64)
timeStr := record[4]
fmt.Println(nodeID, lng, lat, timeStr)
// 時間のパース
var parsedTime time.Time
if timeStr != "" {
parsedTime, _ = time.Parse("15:04:05", timeStr)
}
// データを構造体に格納
data := BusData{
NodeID: nodeID,
Time: parsedTime,
Location: LatLng{
Lat: lat,
Lng: lng,
},
}
busData = append(busData, data)
}
fmt.Println(busData)
}で、かなり、すったもんだした結果、文字列に余分なスペースが含まれていたため であることが分かりました(このくらい自動で対処して欲しいが)。
strings.TrimSpace がキモだったようです。
修正後のプログラムは以下の通り。
package main
import (
"encoding/csv"
"fmt"
"os"
"strconv"
"strings"
"time"
)
// 緯度経度の型定義
type LatLng struct {
Lat, Lng float64
}
// 時間と緯度経度の情報を持つ構造体
type BusData struct {
NodeID int
Time time.Time
Location LatLng
}
func main() {
// CSVファイルを開く
file, err := os.Open("small2_bus_data.csv")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
// CSVファイルの内容をパースする
reader := csv.NewReader(file)
records, err := reader.ReadAll()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
return
}
// データを格納するためのスライス
var busData []BusData
// CSVの各行を処理する
for _, record := range records {
nodeID, _ := strconv.Atoi(record[0])
// スペースをトリムしてから実数に変換
lng, err := strconv.ParseFloat(strings.TrimSpace(record[2]), 64)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error parsing lng:", err)
return
}
lat, err := strconv.ParseFloat(strings.TrimSpace(record[3]), 64)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error parsing lat:", err)
return
}
timeStr := strings.TrimSpace(record[4]) // スペースをトリム
fmt.Println(nodeID, lng, lat, timeStr)
// 時間のパース
var parsedTime time.Time
if timeStr != "" {
parsedTime, err = time.Parse("15:04:05", timeStr)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error parsing time:", err)
return
}
}
// データを構造体に格納
data := BusData{
NodeID: nodeID,
Time: parsedTime,
Location: LatLng{
Lat: lat,
Lng: lng,
},
}
busData = append(busData, data)
}
fmt.Println(busData)
}出力結果は
>go run main28.go
1 139.62957005198 35.36604342344 12:55:00
[{1 0000-01-01 12:55:00 +0000 UTC {35.36604342344 139.62957005198}}]
となり、一安心です。
これが正解か分かりませんが、とりあえず力づくでやりまた。
// NormalizeCoordinates 京急富岡駅を基準として正規化された緯度と経度を返す関数
// C:\Users\ebata\tomioka_school\src\trip_school\NormalizeCoordinates.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func NormalizeCoordinates(referenceLat, referenceLng, lat, lng float64) (float64, float64) {
// 1度あたりの緯度経度のメートル換算
metersPerDegreeLat := 111319.9 // 緯度1度あたりのメートル数
metersPerDegreeLng := 111319.9 * math.Cos(referenceLat*(math.Pi/180.0)) // 経度1度あたりのメートル数
// 緯度と経度の差を計算
deltaLat := lat - referenceLat
deltaLng := lng - referenceLng
// 正規化された緯度と経度を計算
normalizedLat := deltaLat * metersPerDegreeLat / 100.0
normalizedLng := deltaLng * metersPerDegreeLng / 100.0
return normalizedLat, normalizedLng
}
func main() {
// 京急富岡駅の緯度経度
keikyuTomiokaLat := 35.367131726654705
keikyuTomiokaLng := 139.62988318023088
// 確認用の緯度経度(富岡駅のバス停)
lat := 35.36605614545459
lng := 139.6295094178281
// 緯度経度の正規化
normalizedLat, normalizedLng := NormalizeCoordinates(keikyuTomiokaLat, keikyuTomiokaLng, lat, lng)
fmt.Printf("正規化された緯度: %.6f\n", normalizedLat)
fmt.Printf("正規化された経度: %.6f\n", normalizedLng)
}
// NormalizeTime 2つの日時文字列の時間差を秒単位で計算し、600秒を1として正規化する関数
// C:\Users\ebata\tomioka_school\src\trip_school\NormalizeTime.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func NormalizeTime(timeStr1, timeStr2 string) float64 {
layout := "2006-01-02 15:04:05"
t1, err := time.Parse(layout, timeStr1)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error parsing time string 1:", err)
return 0
}
t2, err := time.Parse(layout, timeStr2)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error parsing time string 2:", err)
return 0
}
duration := t2.Sub(t1).Seconds()
normalizedDuration := duration / 600.0
return normalizedDuration
}
func main() {
timeStr1 := "2024-01-01 00:00:00"
timeStr2 := "2024-02-11 23:45:00"
normalized := NormalizeTime(timeStr1, timeStr2)
fmt.Println("正規化された時間差:", normalized)
}