QGISのプラグイン(PosiView)を使って、移動体のリアルタイム表示をする
(display real-time mobile objects using QGIS plug-in (PosiView) )
江端智一のホームページ
QGISのプラグイン(PosiView)を使って、移動体のリアルタイム表示をする
(display real-time mobile objects using QGIS plug-in (PosiView) )
あが
の方法が上手く動かない。
$ tree
.
├── Agent
│ ├── cert.pem
│ ├── go.mod
│ ├── go.sum
│ ├── key.pem
│ └── main.go
├── join
│ ├── cert.pem
│ ├── join.exe
│ ├── join.go
│ └── key.pem
└── ldarp
└── libdarp.goのAgent/main.go と、join/join.goの中で、ldap/libdarp.goを使いたいんだけど、
import (
"m/ldarp"
)を、
import (
"m/../ldarp"
)とか
import (
"m/./../ldarp"
)とか試したみたんだけど、ダメ。
エラーコードに記載されているように、大人しく、
join.go:13:2: package m/ldarp is not in GOROOT (c:\go\src\m\ldarp)
のところに作れば動くんだろうけど、『負けたような気がする』ので、Agent/main.go と、join/join.goの中に、ldap/libdarp.goを埋めこむことで対応した。
ライブラリの二重管理になるけど、まあいいかな、と。
使う度に調べるので、メモしておきます。
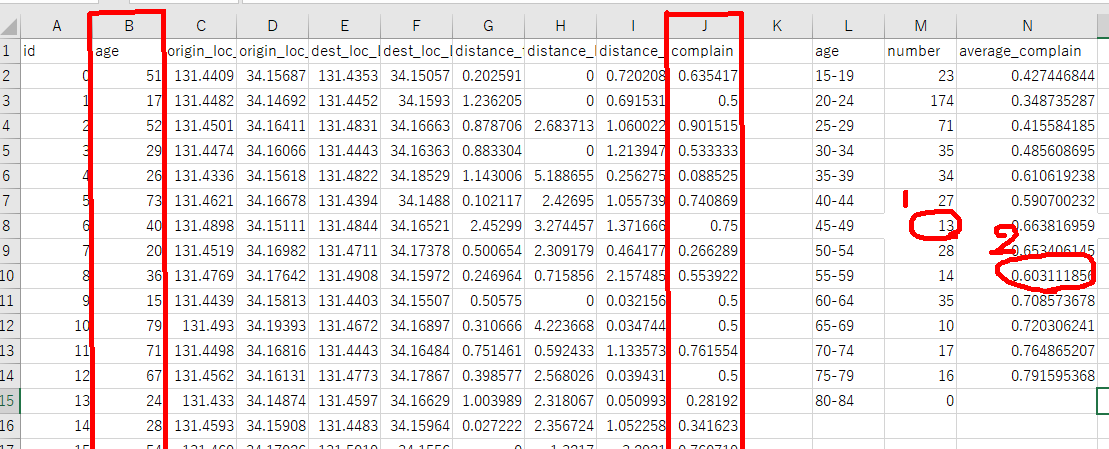
1. 40歳から44歳の人の人数を数えろ
=COUNTIFS($B$1:$B$498, ">=45",$B$1:$B$498, "<50" )
2.55歳から59歳の人の不満値の平均値を求めよ
=AVERAGEIFS($J$1:$J$498, $B$1:$B$498, ">=55",$B$1:$B$498, "<60" )
Keywords: COUNTIF, COUNTIFS, AVERAGEIFS
官能の人工知能 ~深層学習を最も分かりやすく説明するパラダイムOver the AI ―― AIの向こう側に(22)
で使ったソースコード(cpp)が見つからなかったので、添付しておきます。
I could not find the source code (cpp) used in the following, so I am attaching it.
ついでに、破壊実験の方も
Code for destructive experiments
口に出せない介護問題の真実 ~「働き方改革」の問題点とは何なのか
The Truth About Unspoken Nursing Care Issues - What is the Problem with "Workplace Reform"?
This program is based on the following page
https://qiita.com/ufoo68/items/9e4ca04578ba0f5fa5ff
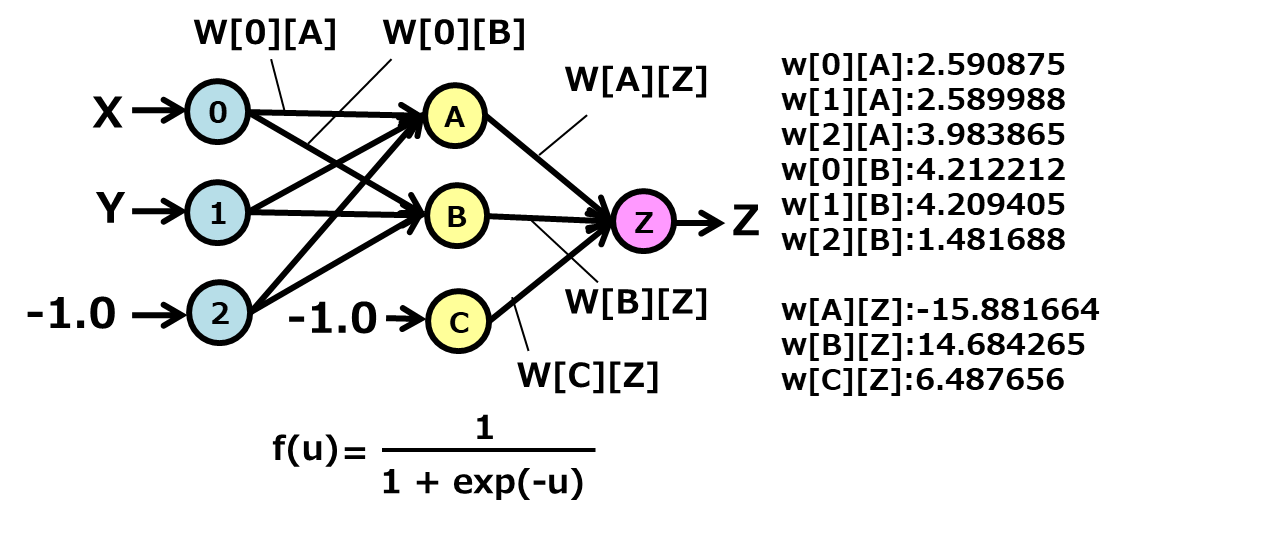
This program solves the XOR problem using MLP with one hidden layer.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//num of units
#define NUM_INPUT 2
//#define NUM_HIDDEN 20
#define NUM_HIDDEN 2
double sigmoid(double x) {
return 1/(1+exp(-x));
}
//derivative of sigmoid function
double d_sigmoid(double x) {
double a = 0.1;
return a*x*(1-x);
}
int main(void) {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
//train data
double train_x[4][NUM_INPUT+1] = {{0, 0, -1},{0, 1, -1},{1, 0, -1},{1, 1, -1}};
double d[4] = {0, 1, 1, 0};
//net
double w[NUM_HIDDEN+1][NUM_INPUT+1];
double v[NUM_HIDDEN+1];
double y[4][NUM_HIDDEN+1];
double z[4];
double eta = 0.1;
int epoch = 1000000;
//other
int i, j, k, l;
double tmp = 0;
//update weights using rand()
for(l=0; l<NUM_HIDDEN+1; l++) {
for(i=0; i<NUM_INPUT+1; i++) {
w[l][i] = ((double)rand() / ((double)RAND_MAX + 1));
}
}
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
v[i] = ((double)rand() / ((double)RAND_MAX + 1));
}
//tain
for(k=0; k<epoch; k++) {
//feedforward
for(j=0; j<4; j++) {
//hidden
for(l=0; l<NUM_HIDDEN; l++) {
for(i=0; i<NUM_INPUT+1; i++) {
tmp += train_x[j][i] * w[l][i];
}
y[j][l] = sigmoid(tmp);
tmp = 0;
}
y[j][NUM_HIDDEN] = -1;
//output
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
tmp += y[j][i] * v[i];
}
z[j] = sigmoid(tmp);
tmp = 0;
//backward
//output
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
v[i] = v[i] - eta * y[j][i] * d_sigmoid(z[j]) * (z[j] - d[j]);
}
//hidden
for(l=0; l<NUM_INPUT+1; l++) {
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
w[i][l] = w[i][l] - eta * train_x[j][l] * d_sigmoid(y[j][i]) * d_sigmoid(z[j]) * (z[j] - d[j]) * v[i];
}
}
}
/*
//print detail
printf("z=");
for(i=0; i<4; i++) {
printf("%f ", z[i]);
}
printf("epoch:%d\n",k);
*/
}
//predict
for(j=0; j<4; j++) {
//hidden
for(l=0; l<NUM_HIDDEN; l++) {
for(i=0; i<NUM_INPUT+1; i++) {
tmp += train_x[j][i] * w[l][i];
}
y[j][l] = sigmoid(tmp);
tmp = 0;
}
y[j][NUM_HIDDEN] = -1;
//output
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
tmp += y[j][i] * v[i];
}
z[j] = sigmoid(tmp);
tmp = 0;
}
//print result
printf("z=");
for(i=0; i<4; i++) {
printf("%f ", z[i]);
}
printf("epoch:%d\n",k);
for(i=0; i<NUM_INPUT+1; i++) {
for(l=0; l<NUM_HIDDEN+1; l++) {
printf("w[%d][%d]:%f\n", i, l, w[i][l]);
}
}
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
printf("v[%d]:%f\n",i, v[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Save this program as a name "mlp.c", compile ">gcc mlp.c" and execute ">./a.exe"
Golang 文字列を数値に変換する方法で、文字列→実数なら、これが一番てっとり早そう
dest_lat, err := strconv.ParseFloat(row[2], 64)
strconv.ParseIntとstrconv.ParseUnitは、文字列を解析して整数型を返す関数
それぞれ符号付き整数型と符号なし整数型に対応している。